Soluble Amyloid Precursor Protein Signals to Neural Stem Cells
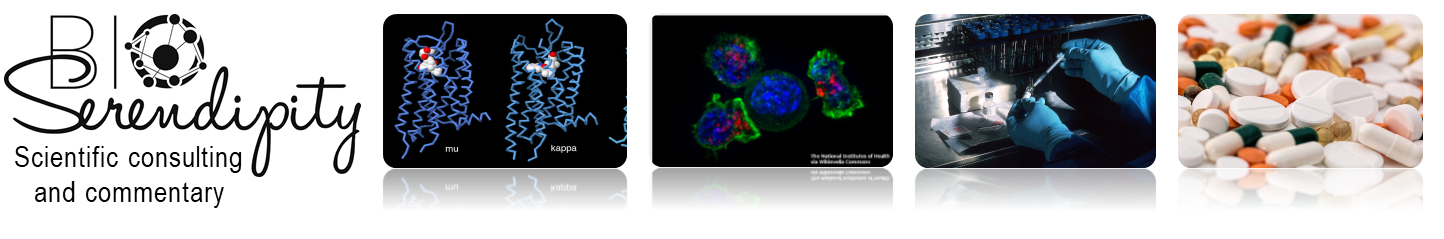
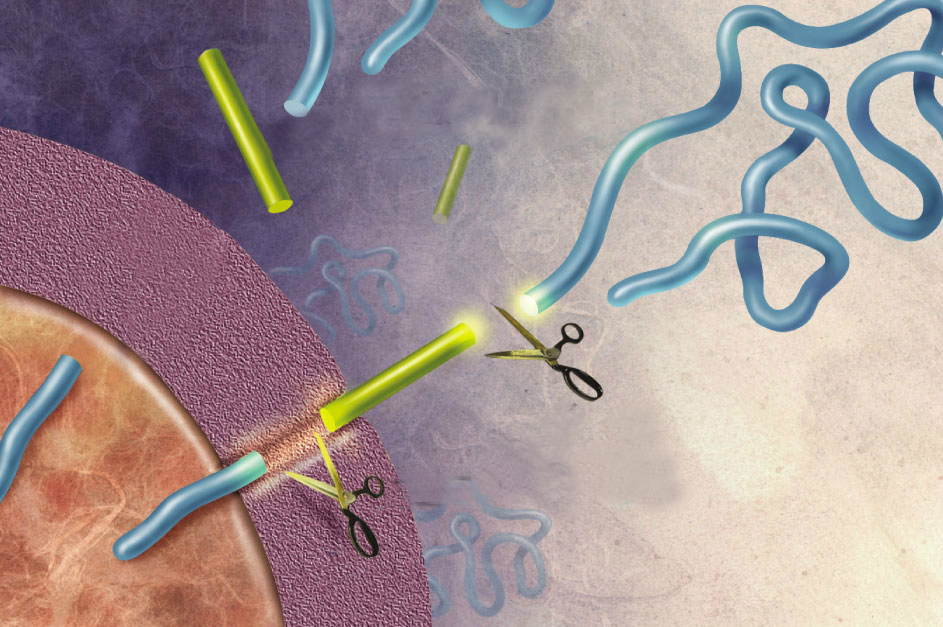
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is best known as the protein that is cleaved to form the plaque-associated protein in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. The APP gene encodes multiple alternatively spliced mRNA forms. The form that encodes a protein of 695 amino acids (APP695) is expressed in neurons. The transcript that encodes a 770 amino … Read more