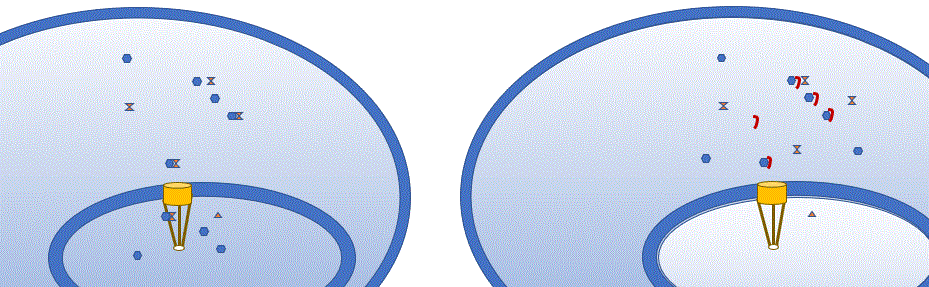
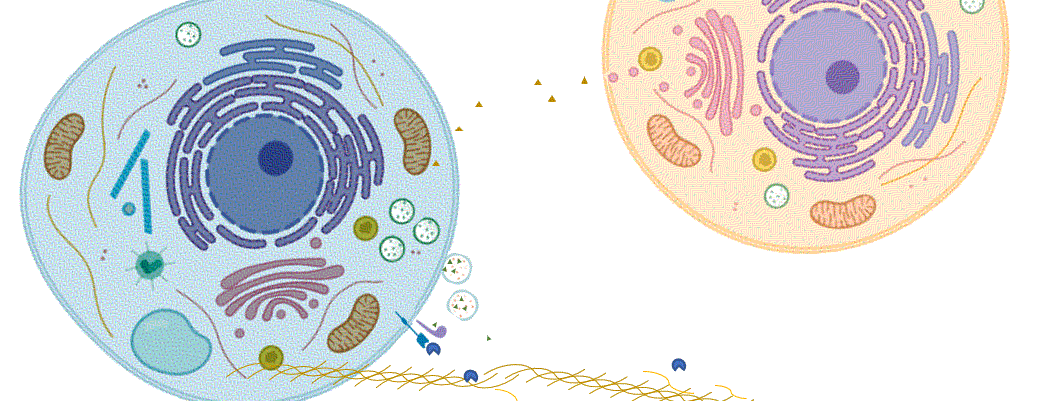
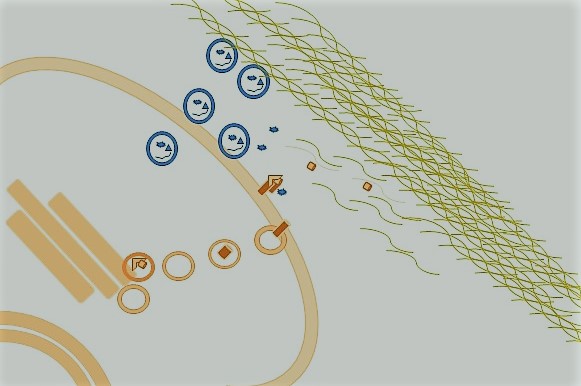
Blocking Nuclear Translocation to Treat Cancer and Colitis
Many proteins have multiple roles. Often, the key to effective therapy is specificity. Not only does the treatment need to be specific for a particular physiological target, often a protein, but the therapeutic effects involve only a single function or subset of the target’s functions or needs to affect the target only within a specific … Read more