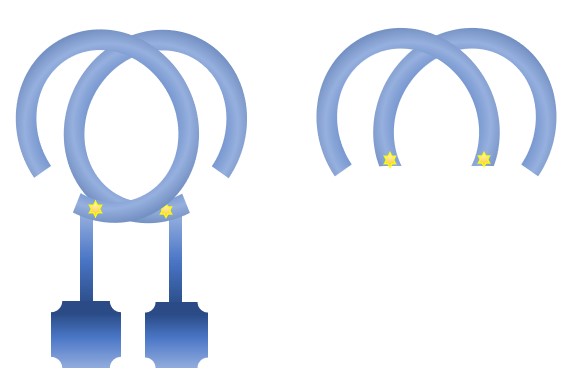
TLR7 is a viral RNA-detecting protein important for stimulating antiviral responses in immune cells. Mutations in the gene encoding this receptor have been found in men who develop severe COVID-19. The cartoon of the protein on the left shows a pair of TLR7 proteins with the position of the mutation [Val795Phe], which means that in the protein the valine at position 795 becomes a phenylalanine. This amino acid is in a part of the protein that is identical in 11 species ranging from man to fish. The mutation is predicted to have a deleterious effect on the function of the protein. The cartoon of the protein on the right shows the truncated version of the protein that would be produced by another variant of the TLR7 gene. In this variant, the mutation [Gln710Argfs*18] causes the amino acid glutamine (Gln) at position 710 to become an arginine (Arg) and then there is a frameshift (fs) mutation that results in a STOP codon (*) so that the protein terminates after 18 more amino acids (*18). Thus, the resulting protein is truncated and missing several parts that are critical for its function. The mutations are indicated by yellow stars.
Read more: TLR7 Mutations Are Associated with Severe COVID-19
Read all COVID-19 articles