Odor Battles: From Corn to Caterpillar to Wasp
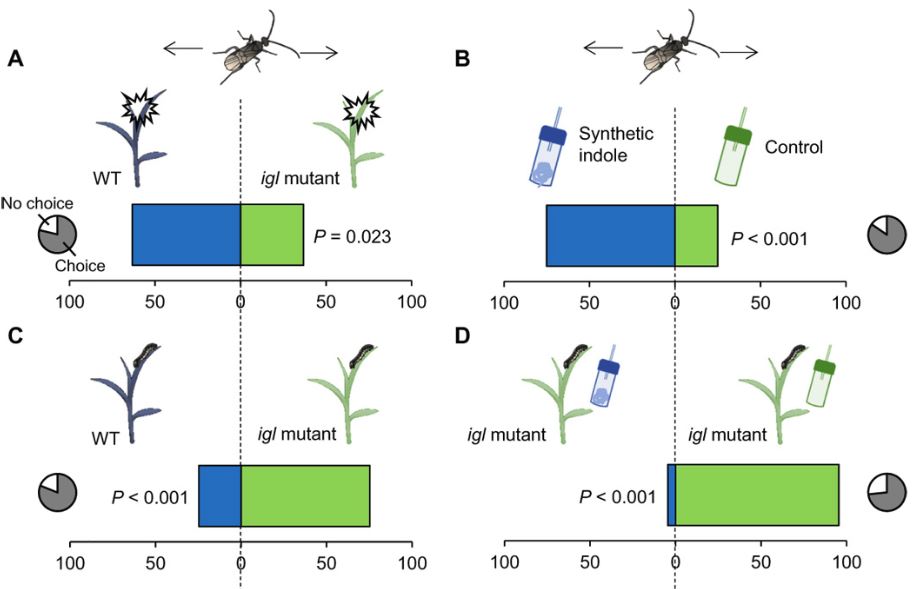
In nature, insect herbivores eat plants and other insects parasitize the herbivore insects, creating a tritrophic system. Ye and colleagues investigated how volatile chemicals (odorant molecules) affect one such tritrophic system—corn herbivory by moth larvae (caterpillars) of Spodoptera littoralis and the parasitism of the caterpillars by the wasp Microplitis rufiventris (Figure 1). The moth lays eggs … Read more